hot100系列——链表
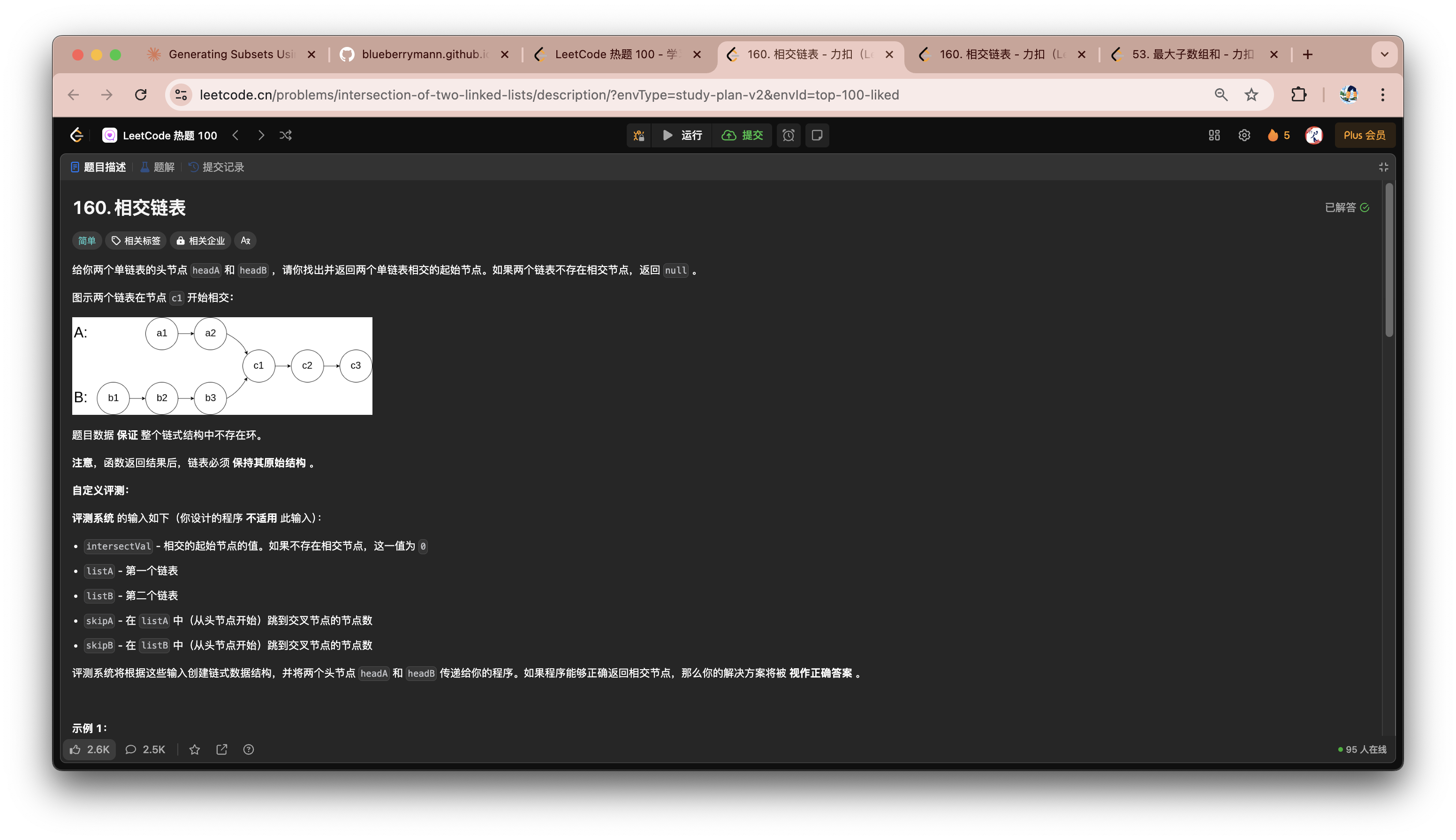
相交链表
知识点
-
unordered_set是一个集合,也称为哈希集合- 只存储单个值(与
unordered_map区分) - 每个元素都是唯一的
- 元素不能修改,只能插入或者删除
- 主要用于快速检查元素是否存在
- 只存储单个值(与
-
unorderd_set的count操作是用来查找集合中元素的个数的,由于unorderd_set中的元素都是唯一的,所以count操作的返回值只有0或1
解题思路
- 首先遍历链表A,并将链表A中的中的每一个节点存入
unordered_set中 - 接下来遍历链表B,使用
count操作判断该节点是否在链表A中也存在- 如果存在,则说明该节点即为相交节点
- 如果不存在,则继续遍历
实现代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
unordered_set<ListNode *> visited;
ListNode *temp = headA;
while(temp != nullptr){
visited.insert(temp);
temp = temp -> next;
}
temp = headB;
while(temp != nullptr){
if(visited.count(temp))
return temp;
temp = temp -> next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
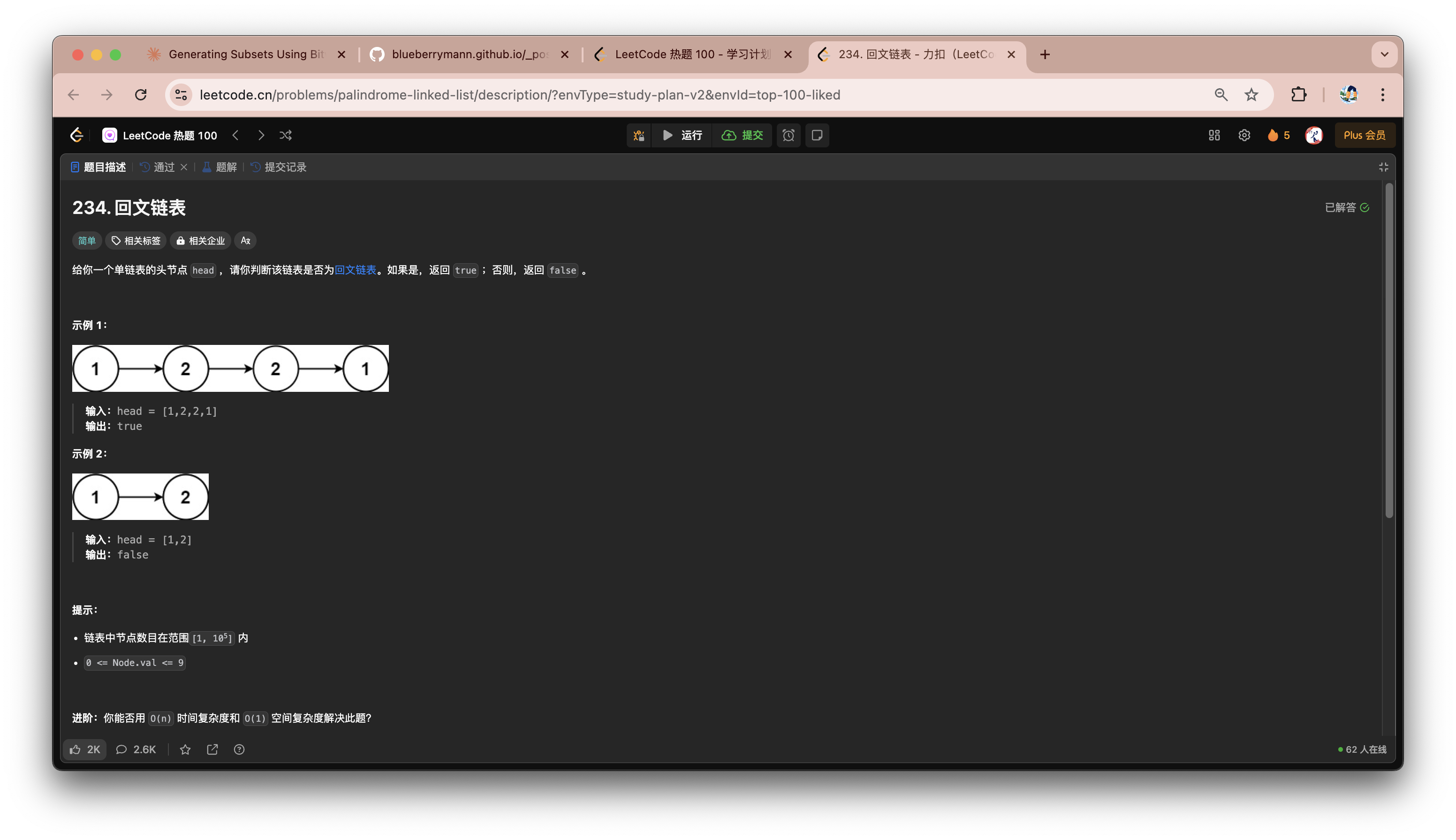
回文链表
知识点
- 需要解决回文字符串的前序知识
解题思路
- 将链表遍历,每个节点的值存入数组中
- 初始化左指针
l = 0,右指针r = list.size() - 1,分别从数组两端进行遍历,直到l >= r- 如果指针指向的两个字母不相同,那么返回
false - 如果遍历完整结束,则返回
true
- 如果指针指向的两个字母不相同,那么返回
实现代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> list;
ListNode *temp;
temp = head;
while(temp != nullptr){
list.push_back(temp -> val);
temp = temp -> next;
}
int l = 0, r = list.size() - 1;
while(l < r){
if(list[l] != list[r])
return false;
l ++;
r --;
}
return true;
}
};
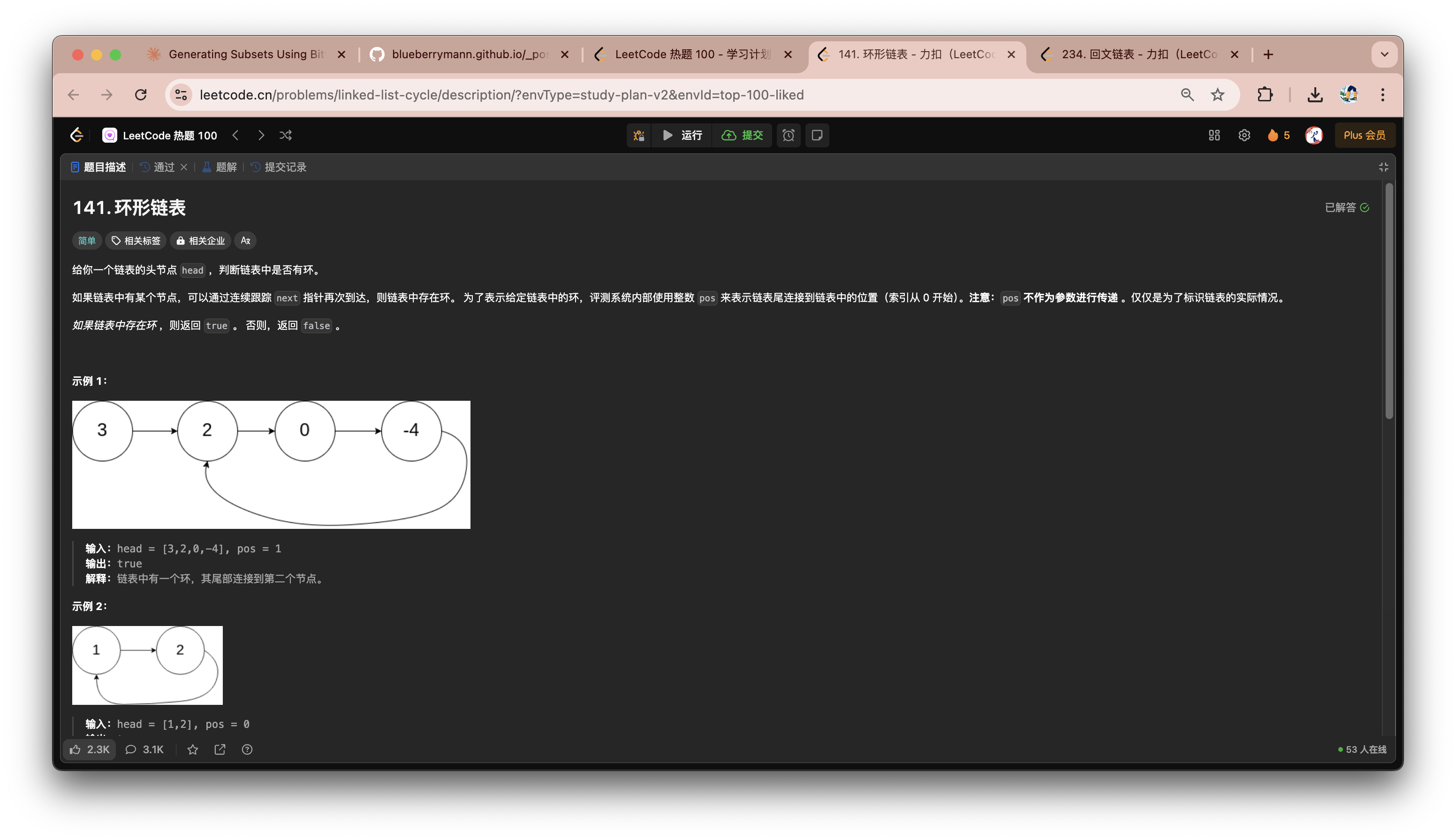
环形链表
知识点
- 需要相交链表的前序知识
解题思路
- 初始化一个
unordered_set用于存储已经遍历过的结点 - 每次遍历前首先判断一下这个节点是否已经在
unordered_set中- 如果已经在
unordered_set中,说明链表有重复部分(环),则返回true - 如果遍历到指针为空,则说明无环,返回
false
- 如果已经在
实现代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_set<ListNode *> visited;
ListNode *temp = head;
while(temp != nullptr){
if(visited.count(temp)){
return true;
}
visited.insert(temp);
temp = temp -> next;
}
return false;
}
};
环形链表II
合并两个有序链表
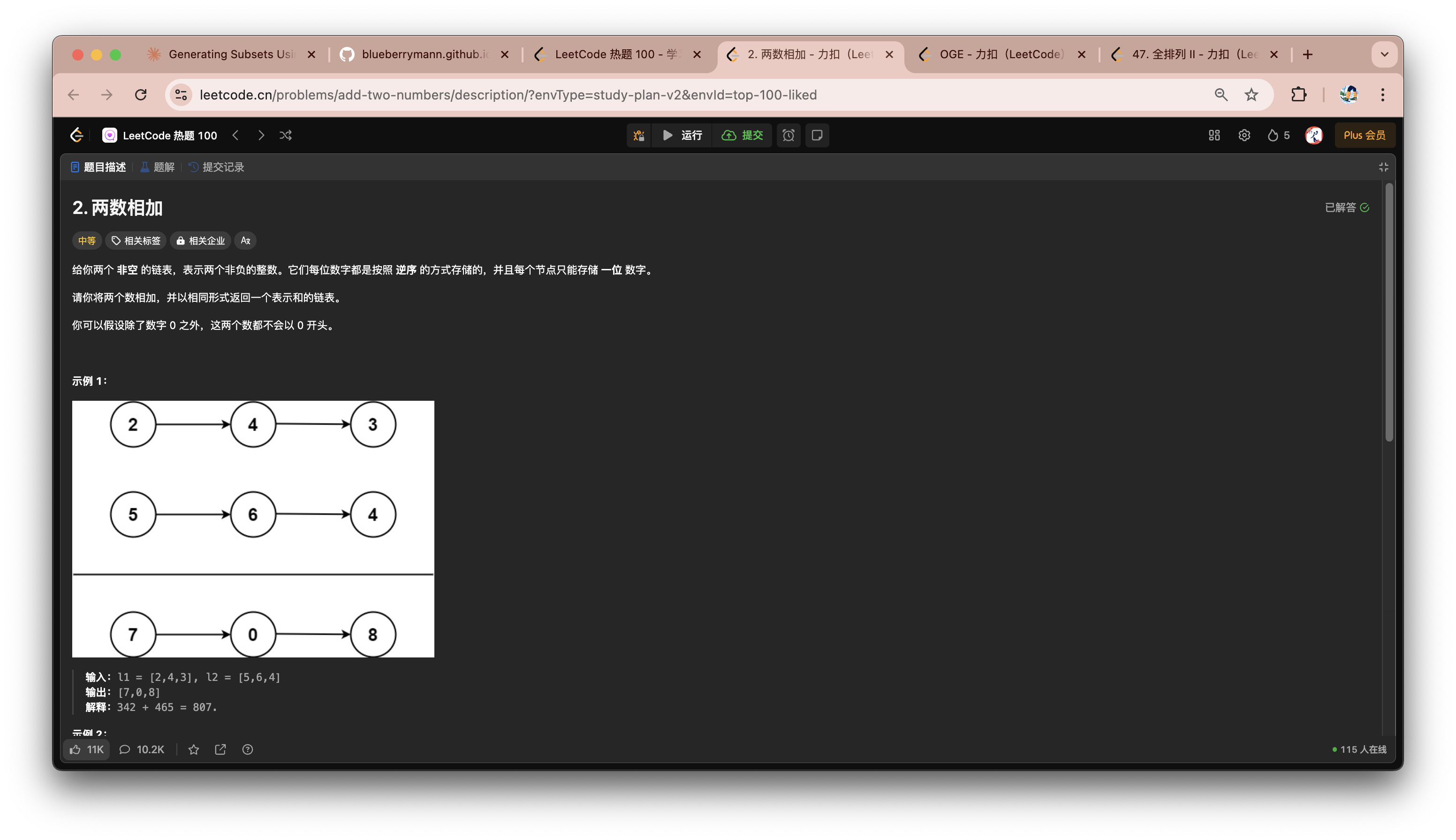
两数相加
知识点
- AcWing大数相加模版
解题思路
- 将两个链表转化为数组存储
- 使用大数相加模版
实现代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* add(vector<int> a, vector<int> b){
ListNode *ans = new ListNode();
vector<int> c;
int r = 0;
int d = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i ++){
if(i < b.size()){
d = (a[i] + b[i] + r) % 10;
r = (a[i] + b[i] + r) / 10;
c.push_back(d);
}else{
d = (a[i] + r) % 10;
r = (a[i] + r) / 10;
c.push_back(d);
}
}
if(r){
c.push_back(r);
}
ListNode *cur = ans;
for(auto num: c){
ListNode *nxt = new ListNode(num);
cur -> next = nxt;
cur = nxt;
}
return ans->next;
}
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
vector<int> a, b;
ListNode *temp = l1;
while(temp != nullptr){
a.push_back(temp -> val);
temp = temp -> next;
}
temp = l2;
while(temp != nullptr){
b.push_back(temp -> val);
temp = temp -> next;
}
if(a.size() > b.size()){
return add(a, b);
}else{
return add(b, a);
}
}
};
删除链表的倒数第N个节点
知识点
- 哑结点:在链表操作中,为了避免处理头节点的特殊情况,通常会创建一个哑结点(dummy node)作为链表的新头部。哑结点的值通常不重要,它的next指针指向原链表的头节点。这样在删除或插入操作时,可以统一处理所有节点,包括原始的头节点,简化代码逻辑。
- 双指针技巧:可以使用快慢指针找到倒数第N个节点。让快指针先走N步,然后快慢指针一起走,当快指针到达链表末尾时,慢指针正好指向倒数第N个节点的前一个节点。
- 链表长度计算:通过遍历链表可以获取链表的总长度,然后可以计算出倒数第N个节点是正数第(length-N+1)个节点。
解题思路
实现代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int getLength(ListNode *head){
int length = 0;
while(head){
++ length;
head = head->next;
}
return length;
}
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
int length = getLength(head);
ListNode *cur = dummy;
for(int i = 1; i < length - n + 1; i ++){
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = cur->next->next;
ListNode *ans = dummy->next;
delete dummy;
return ans;
}
};
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: