区间和
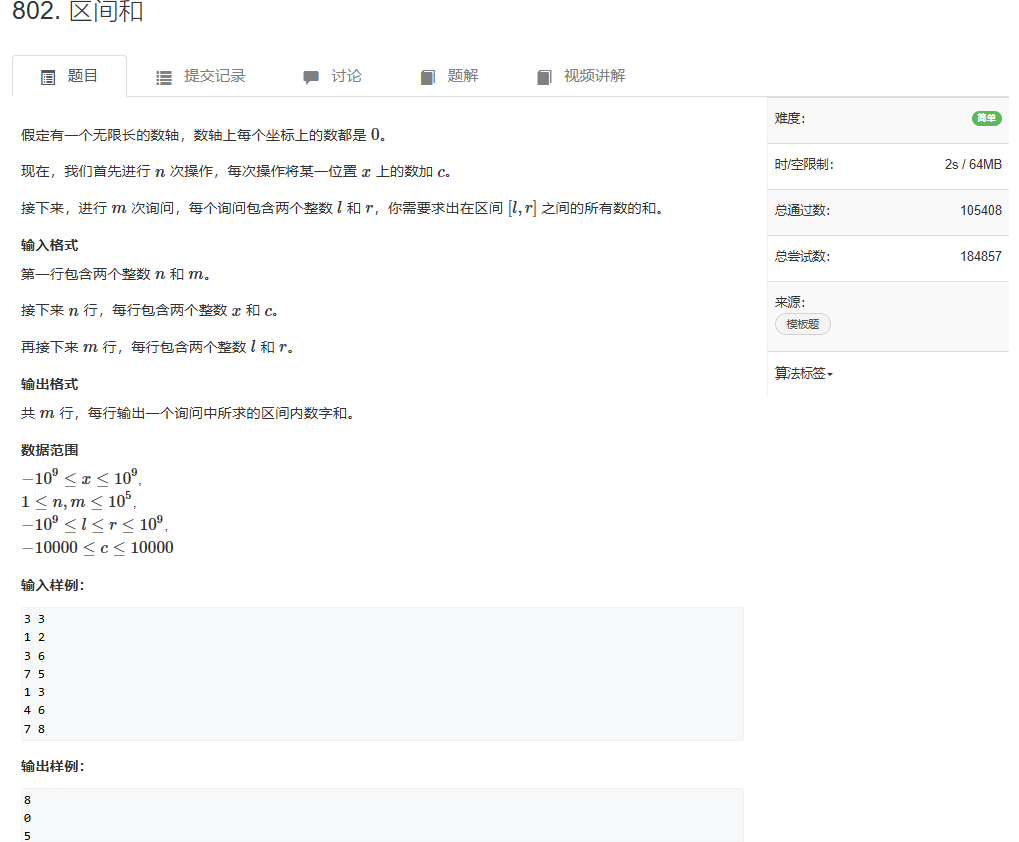
离散化
1, 3, 5, ..., 1e9
- 有几个数字,数值的范围特别大,但是个数比较少。
- 有时候需要将数值特别大的数字作为下标使用,但是由于数值特别大,我们的存储空间无法满足要求
- 所以我们要将这几个数字与连续的自然数建立映射
- 这个就叫做离散化
| a[] | 1 | 3 | 5 | 100000 | 50000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
存在的问题
-
a[]中可能有重复的元素,需要去重 - 如何算出
x离散化后的值
解决问题
去重
- 在
c++中,我们有一个专用的套路去除vector中的所有元素
vector<int> alls;
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end());
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end());
解题思路
- 目前给定的数轴太长了,数据范围是[-1e9, 1e9]
- 经过我们的分析,在这个数轴上,我们最多最多只能用到$3\times 1e5$个数
- 所以我们要将这$3\times 1e5$的下标,排序后映射到从1开始的自然数
- 假设下标映射后为k,那么我们让
a[k] += c - 那么我们该如何确定某个下标的映射
k为多少呢?我们利用二分查找构建find函数,使用该函数在排好序、去好重的alls数组中进行查找,查找的内容就是这个下标映射的自然数位置 - 通过以上这种方法,将插入操作和查询操作中的离散的下标都转化为了连续的、稠密的自然数下标
- 之后利用前缀和进行求解
实现代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3 * 1e5 + 100;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n, m;
int a[N], s[N];
vector<int> alls;
vector<PII> add, query;
int find(int x){
// 这个二分find的目的是找到数字插入的位置
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while(l < r){
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(alls[mid] >= x)
// 这里需要研究一下
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
return r + 1;
}
int main(void){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i< n; i ++){
int x, c;
cin >> x >> c;
add.push_back({x, c});
alls.push_back(x);
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++){
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
query.push_back({l, r});
alls.push_back(l);
alls.push_back(r);
}
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end());
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end());
for(auto item: add){
int x = find(item.first);
a[x] += item.second;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= alls.size(); i ++){
s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
}
for(auto item: query){
int l = find(item.first);
int r = find(item.second);
cout << s[r] - s[l - 1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: